
|
Varian's Gradient Shimming Pulse Sequence
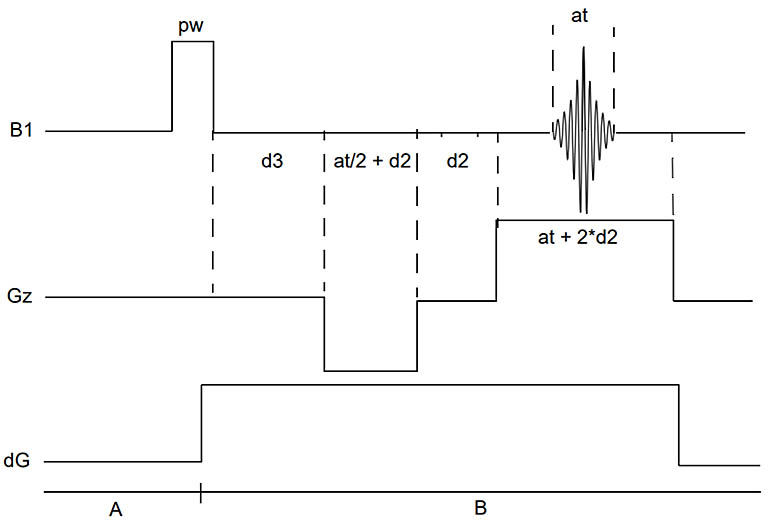 Here d2 = 1 msec. Acquisition time at is ~ 2.5 msec for 1H and
~ 17 msec for 2H shimming. Gz is PFG used to spatially encode spins along Z.
dG represents the combined shims or simply the change of
one shim gradient as the experiment is designed to do with each detection. For each shim change, d3 is arrayed, set to 0 and a ~ 5-10 msec delay, and a spectrum
is acquired with each shim setting, Z1 to Z5. With all
other pulses and delays being equal, the difference
between the two spectra collected with the two d3 values gives Δ(Δφ(z)) = γdG(z)*d3 for
each shim. The dGz curves are the shim map of the probe.
|
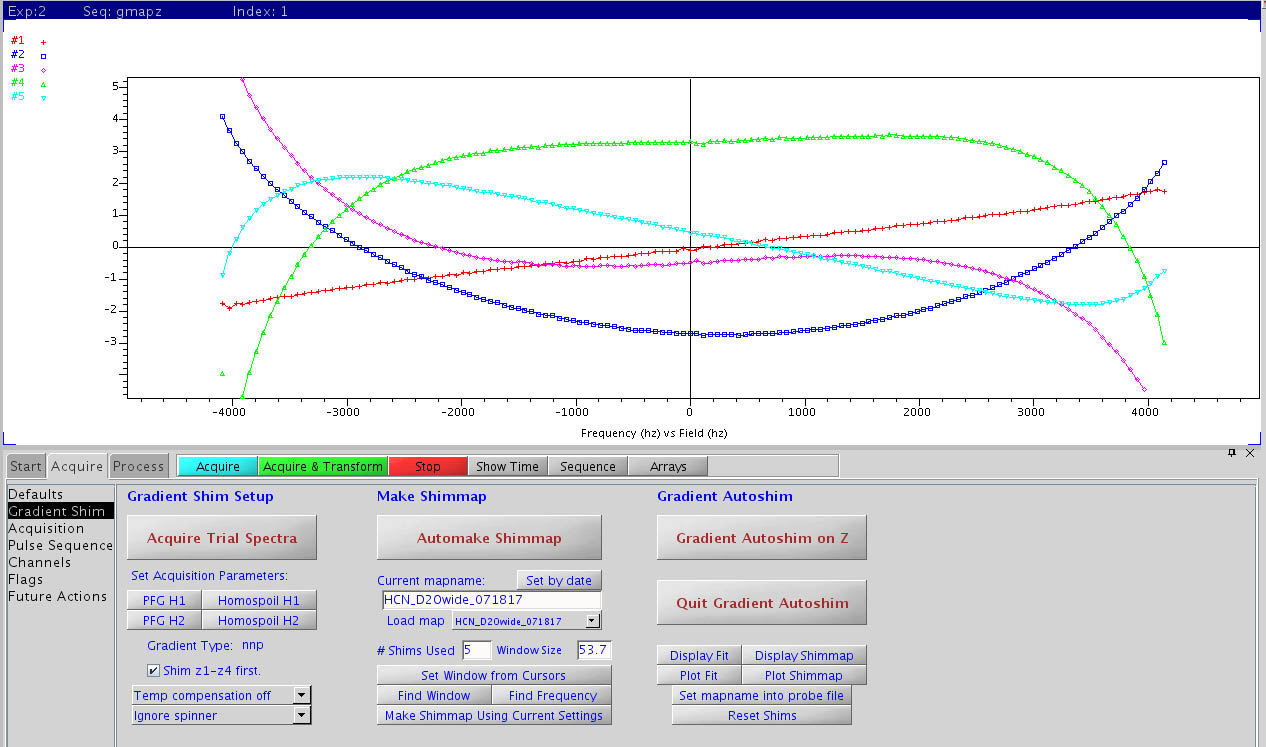 Shim map Created with 2H Detection. The sample has 99% D2O with 1% H2O.
Each shim, Z1 to Z5, has
a unique shape that is designed to give a field shape of an independent, specific order of harmonic function. The actual
profile of each shim as a function of Z (freqency encoded horizontal axis) is measured with the method in the right figure. |
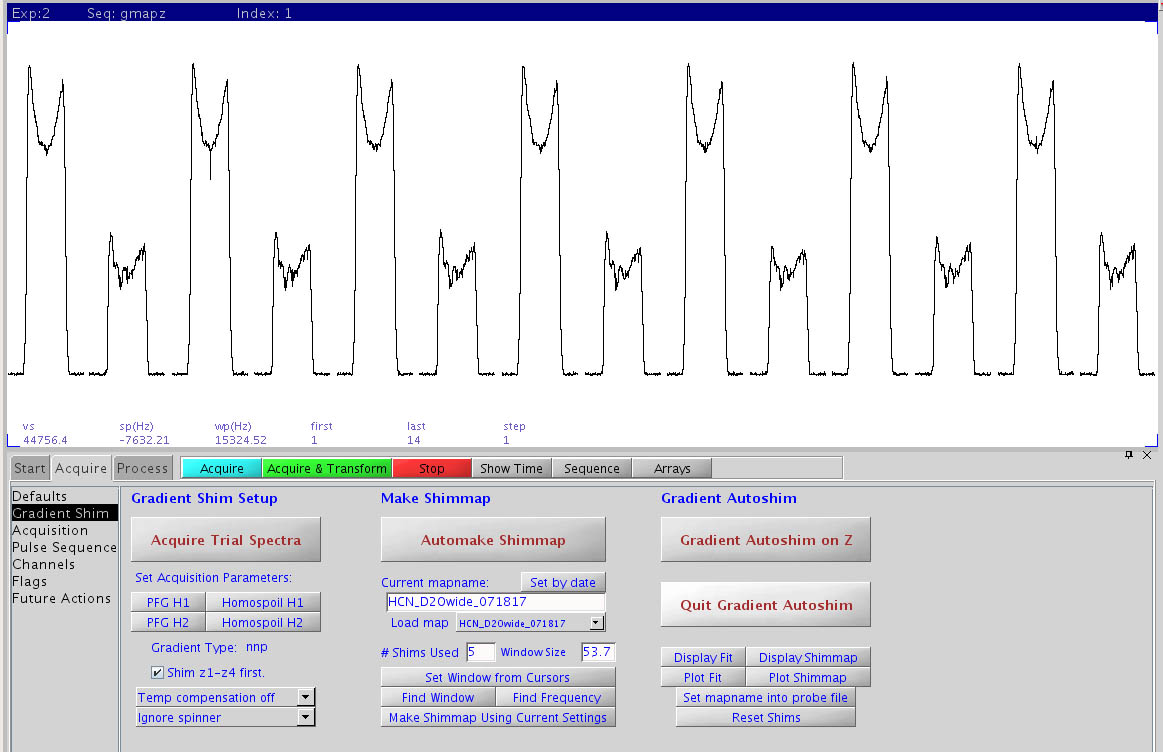 Mapping the shim profiles of Z1 to Z5. The shim values are varied with
~ 1000 DAC unit change within each pair of curves, from Z1 to Z5, starting from current shims. The first
and last pairs of curves are using the current shim values. Within each pair, the delay d3 is varied
from zero to a set value (~ 250 msec here). The difference between the two curves gives the profile of the
shim that is varied within the pair according to equation (2) above.
The differences between the pairs are not obvious because it is the phase of the time-domain data that is extracted to give the individual shim profiles on the left (see equations 1-2 above). The plots shown during Varian's mapping protocol are obviously in magnitude mode that removes the phase data. |
|
Autoshim Fitting
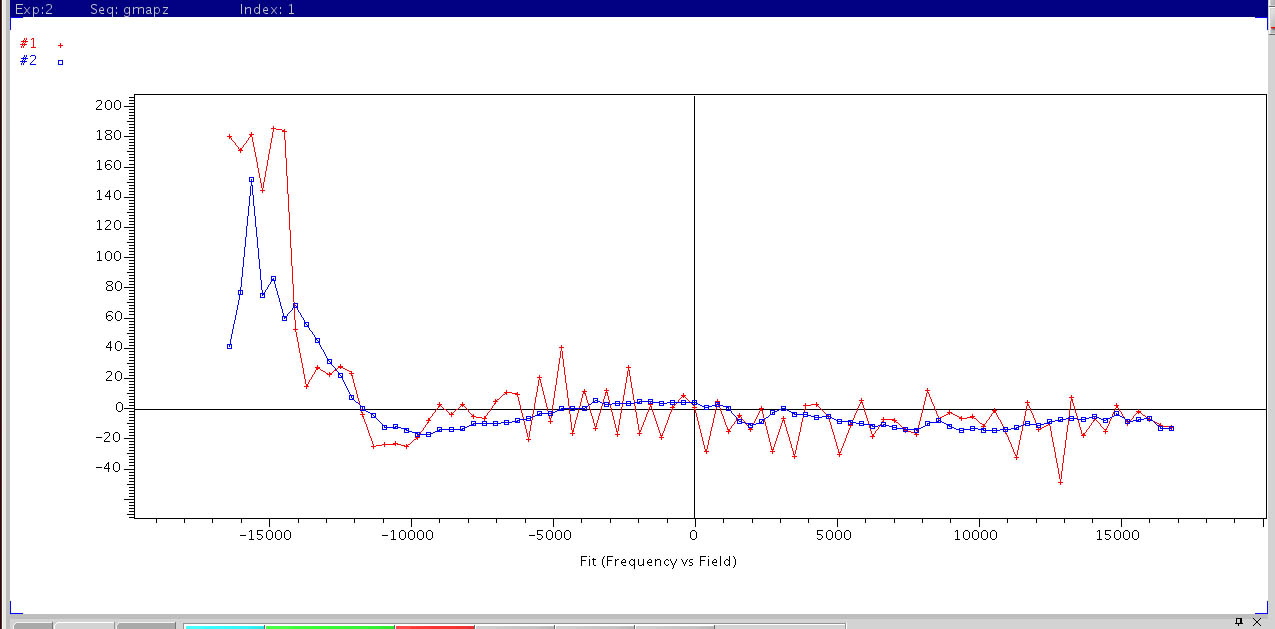 Autoshim on Z. During autoshimming, a linear combination of changes in Z1 to Z5 are applied
according to the shim profile curves with the goal of removing field variations across the sample area. Shown above
are the detected field maps of the last two iterative fittings which have converged to meet a target criteria. The vertical axis
is the calculated field variation in Hz. The horizontal axis is the position encoded frequency along Z in Hz with
the center of the NMR tube at 0 Hz.
|