
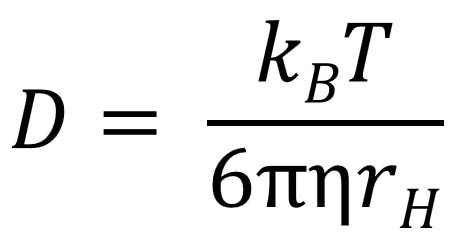
 A simple DOSY pulse sequence using a spin echo (SE). The 90-degree pulse
flips the spins into the transverse plane followed by position/phase encoding by
the gradient pulse.
The 180 degree pulse reverses the sign of the phase changes from the first gradient pulse,
which are subsequently canceled by the second gradient pulse unless the spins have diffused over
the delay period Δ. The loss of the signal intensity as a function of diffusion delay
is measured and processed. In this experiment, diffusion occurs while the spins are
in the transverse XY plane. As usual, chemical shift evolution, but not homonuclear J-coupling, is refocused at the beginning
of the echo by the 180-degree pulse. |
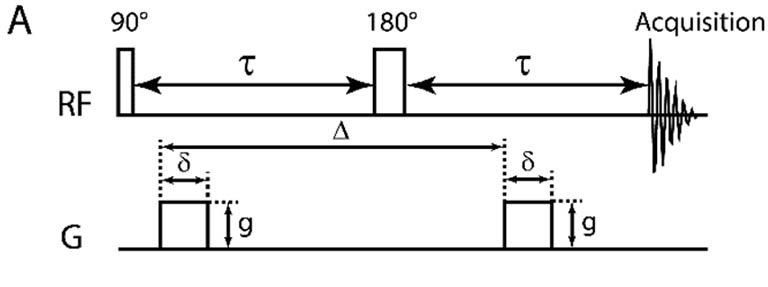
 DOSY with stimulated spin echo (STE). The first 90-degree pulse flips the spins into
XY plane. The first gradient then encodes the spins with position dependent phase changes before the
second 90-degree pulse flips the
spatially labeled spins to Z for diffusion over Δ delay. The third 90-degree pulse
flips the stored spins back into XY plane. The second
gradient cancels the phase changes done by the first one and enables an echo, leaving only the signal
amplitude drop from diffusion. The last two 90-degree pulses act like a 180-degree pulse to reverse
the spin phase changes by the gradient pulses to form the echo. |
|
Magnetogyric Ratios of Commonly Detected Nuclei* (γ, unit: 1000 rad·s-1·G-1)
|
Other Typical, Instrument and Pulse Sequence Dependent Parameters Used in DOSY
|
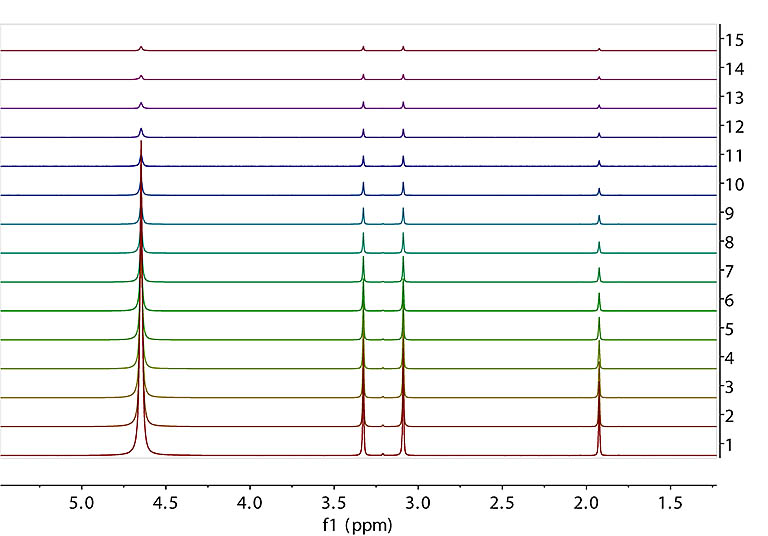 DOSY FID array with varying gradient strength and fixed diffusion time. Data were
collected on our 600 MHz spectrometer with Varian's DgcsteSL_cc sequence
from a sample of 1% H2O (~4.7 ppm), 0.1% 13C labeled methanol (doublet at ~ 3.3 ppm),
and 0.1% 15N labeled acetonitrile (~ 2ppm) in 99% D2O. From bottom to top,
the gradient strength is set to 500, 8039, 11358, 13906, 16055, 17948, 19660, 21234, 22699, 24075, 25377, 26615, 27798,
28933 and 30025 in DAC unit. The maximum gradient (~ 70 Gauss/cm) has a DAC value of 32768. The diffusion time (Δ) is ~ 30 msec.
Recommended signal decay range to measure is from ~ 90% of full intensity with the weakest gradient down to ~ 10% with the maximum gradient. |
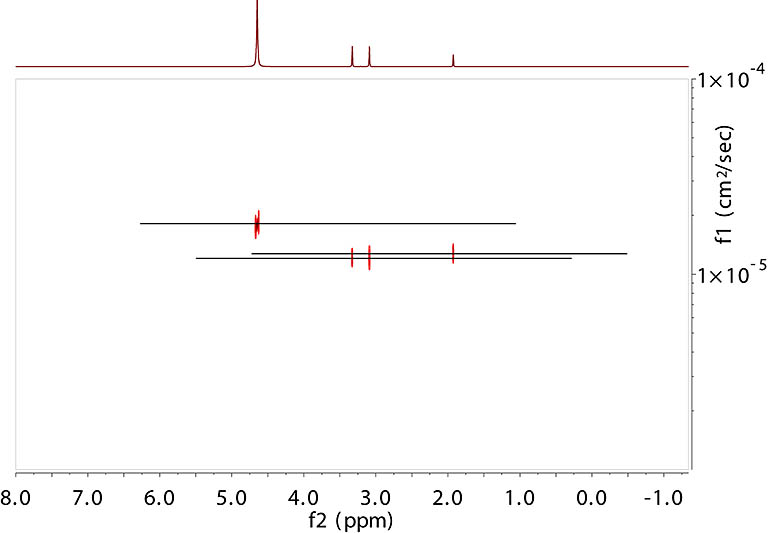 Processed DOSY spectrum. The vertical axis is
the diffusion coefficient (uncalibrated). Data are processed with Mnova using its Bayesian method. |
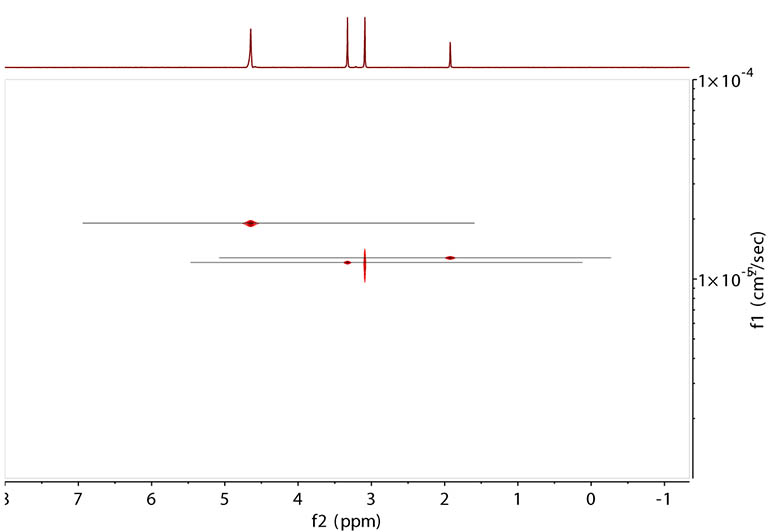 Same data processed with the alternative peak fitting method in Mnova. |
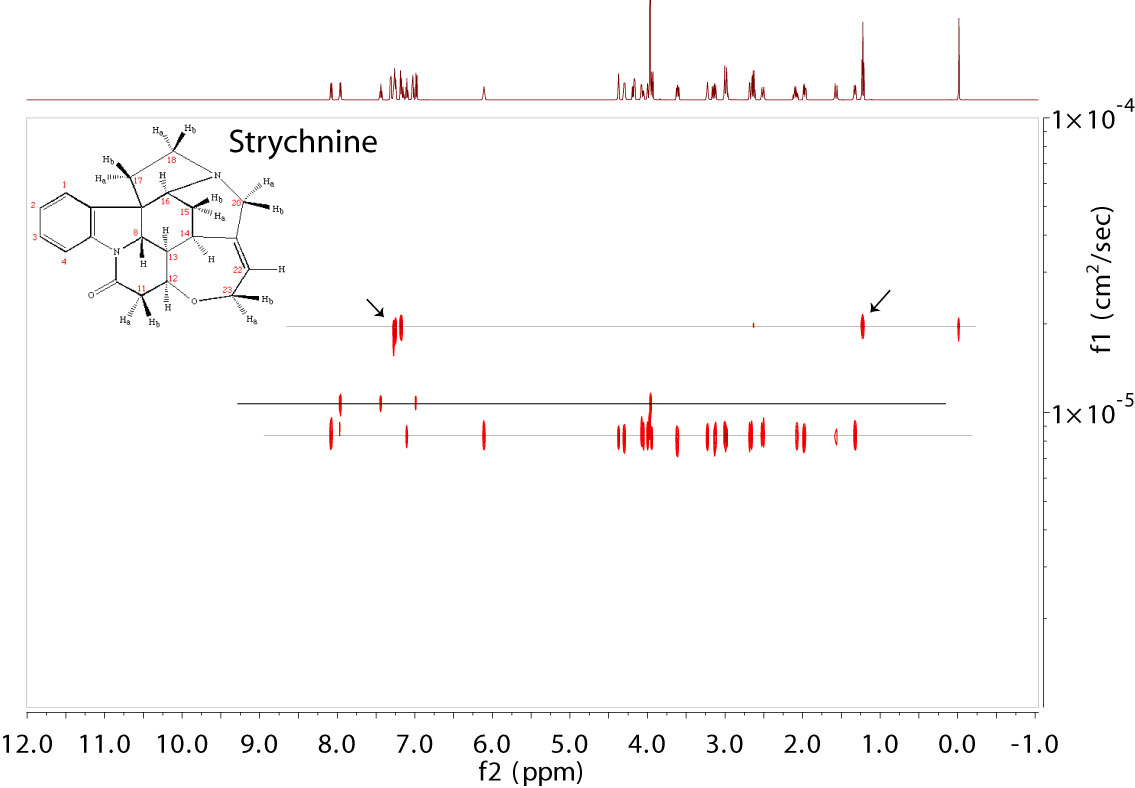 DOSY from a Strychnine sample in CDCl3. The chemical had decomposed
and gave several extra peaks from the decomposed product marked by the solid line and arrows along the top line.
TMS was present at 0 ppm. Residual 1H
signal from chloroform was seen at 7.24 ppm. The data were collected with Varian's Dbppste_cc sequence (right) at 600 MHz and processed
in Mnova with the Bayesian method. |
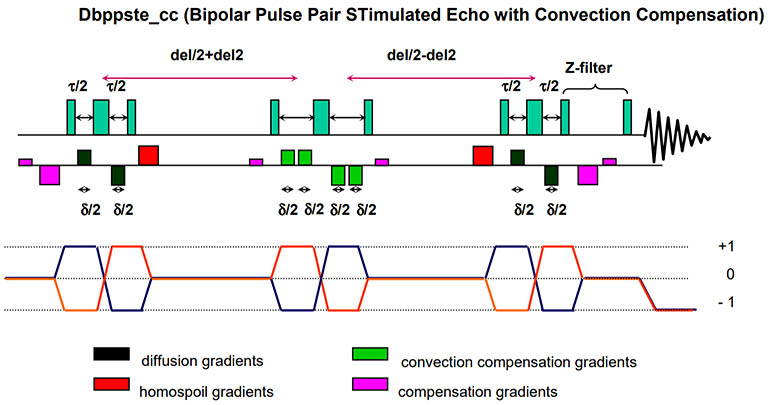 Varian's Dbppste_cc pulse sequence with convection compensation. Convection is
a macroscopic fluid flow resulting from a temperature gradient across the sample. It significantly distorts
molecular diffusion and data quality.
Convection compensation with gradient pulses minimizes this effect. However, the maneuver contains an
extra stimulated echo step and therefore has an inherent, additional 50% signal attenuation with respect to
its equivalent without convection compensation. It may not be suitable for samples with low SNR.
Tricks to minimize convection include disconnecting all air flow into the probe sample area, turning off temperature regulation and using a shorter sample with less volume. |